
low cash on hand), a red flag that could potentially result in the company being in urgent need of restructuring or filing for bankruptcy protection. In the latter scenario, the company is facing a shortage in liquidity (i.e.
Ap turnover days how to#
How to Interpret Payables Turnover Ratio (High vs. to reinvest into operations, for capital expenditures). their branding, reputation, and order volume (and size) can all be leveraged to defer supplier payments.įrom the date when the credit purchase was made to the date that the company actually paid the supplier in cash, the cash remains in the possession of the buyer, who has the discretion to spend that cash in the meantime (e.g.
Ap turnover days free#
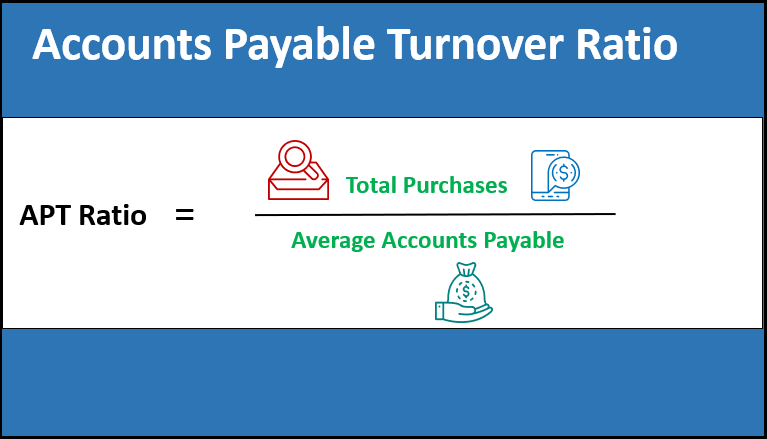
Low A/P Turnover and High DPO ➝ High Bargaining Leverage and More Free Cash Flow (FCF)Ĭompanies like Amazon and Walmart extend their payables outstanding for that reason, i.e.High A/P Turnover and Low DPO ➝ Low Bargaining Leverage and Less Free Cash Flow (FCF).their relationship with their suppliers). The A/P turnover ratio and the DPO are often a proxy for determining the bargaining power of a specific company (i.e. The more a supplier relies on a customer, the more negotiating leverage the buyer holds – which is reflected by a higher DPO and lower A/P turnover. The days payable outstanding (DPO) metric is closely related to the accounts payable turnover ratio.ĭPO counts the average number of days it takes a company to pay off its outstanding supplier invoices for purchases made on credit. So the higher the ratio, the more frequently a company’s invoices owed to suppliers are fulfilled. “How often does the company pay off its invoices per year on average?”įor example, if a company’s A/P turnover is 2.0x, then this means it pays off all of its outstanding invoices every six months on average, i.e.The formula for calculating the accounts payable turnover is as follows.Īccounts Payables Turnover = Supplier Credit Purchases ÷ Average Accounts Payable Average Accounts Payable = (Ending AP + Beginning AP) ÷ 2.
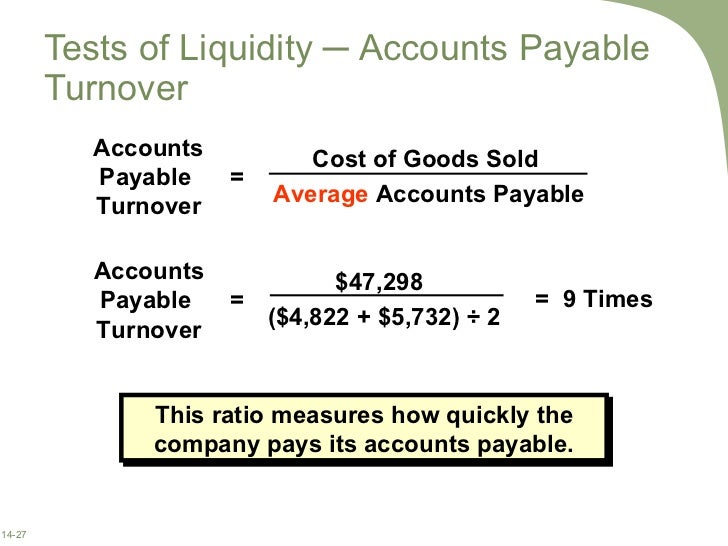
Moreover, the “Average Accounts Payable” equals the sum of the beginning of period and end of period carrying balances, divided by two.
Ap turnover days full#
The total supplier purchase amount should ideally only consist of credit purchases, but the gross purchases from suppliers can be used if the full payment details are not readily available. The “Supplier Credit Purchases” refers to the total amount spent ordering from suppliers. the frequency at which a company pays off its accounts payable balance.Ĭalculating the accounts payable ratio consists of dividing a company’s total supplier credit purchases by its average accounts payable balance. The accounts payable turnover, or “payables turnover”, is a ratio used to evaluate how quickly a company repaid those that offered them a line of credit, i.e. How to Calculate Accounts Payables Turnover (Step-by-Step)Īs part of the normal course of business, companies are often provided short-term lines of credit from creditors, namely suppliers.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
